Your Network's Edge®
Solution & Technology Videos
You are here
Ethernet Service Activation Test: Manage & Orchestrate with RAD
Today’s networks are expected to be open, automated and support agile service delivery. The key to ensuring that in a cost-effective manner lies in the management system and ethernet service activation testing.
In this presentation, we will take a look at RADview, RAD’s network management and orchestration solution.
RADview is a comprehensive network management suite for RAD’s Service Assured Access and Service Assured Networking solutions. Working closely with network operators around the world has provided valuable input that greatly contributed to the development of RADview. Best of all, it is designed to efficiently control large heterogeneous networks based on RAD’s products, while ensuring reliable service delivery with deep visibility into network and service performance.
RADview combines updated HTML5 design principles with an intuitive web client to deliver the best user experience in the market. The progressive web client is designed to simplify complex everyday tasks at the control room and allows a one-click transition from offline planning to a live service.
RADview provides secure interfaces for network managers and allows setup and management of protected business services with encrypted communications.
RADview also uses automation, open-source software components and standard APIs to accelerate service and application activation, as well as to allow easy maintenance and upgrades.
As a modular management suite, RADview provides all required functionality via 4 modules:
- EMS, or element management system to control the network at the device-level, featuring full FCAPS support
- Service manager, to plan and provision Ethernet services, such as E-LINE, E-LAN, E-Tree, and E-Access, as well as TDM services
- Performance monitoring portal, to test, collect and present key performance indicators for Layer 2 and Layer 3 services, including monthly and real-time reporting
- And lastly, the D-NFV Orchestrator, which handles all aspects of network functions virtualization
In addition to these 4 RADview modules, RAD offers a standalone shelf-view application – a local craft terminal and graphical application for onsite technicians.
Let’s take a closer look at the various modules.
The EMS provides remote connectivity to network devices, to perform essential configuration and monitoring tasks. Auto-discovery and zero-touch capabilities allow quick and easy access to the various network elements, to monitor device health and manage user access authorization and authentication. As a mediation layer between the network and OSS/BSS systems, the RADview is interoperable with leading third-party umbrella systems. It is a Java-based solution supporting both Windows and Linux, and is scalable to handle thousands of devices. Designed to provide High Availability and disaster recovery, it also features multi-user support, allowing different users to operate different network domains simultaneously.
All these strengths help optimize network operations and minimize mean time to repair.
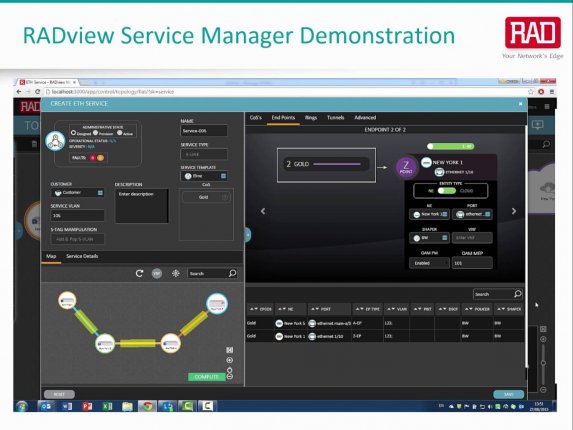
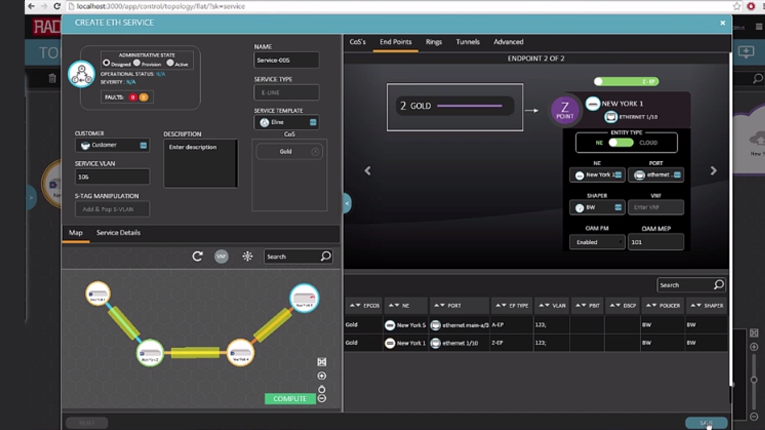
The RADview Service Manager offers “point-and-click”, end-to-end service provisioning with great flexibility. Service providers and network operators can either define service parameters on the fly, or work with predefined templates for services sharing a common pattern. You can select service end-points, set up classification, VLAN manipulation and OAM settings, then view the service route and run ethernet service activation tests.
Moreover, use the Service Manager to plan topologies and services offline before embarking on field deployment, simulating specific network conditions and expected behavior. Once the devices are actually deployed and connected, simply change status from “plan” to “active” in a single click, and the RADview will download all necessary configuration details to the network.
Let’s see an example of service setup:
- To create a new service, we first select two end-point devices, then choose the service type and identify the customer.
- We then set the value of the service VLAN and select the associated classes of service for this particular customer. For each class of service, we set the value of incoming VLAN for classification.
- Our next step is to select the physical port on every end point device.
- When clicking the COMPUTE button, RADview will calculate the route of the service and allocate the required resources.
- We end the process by clicking the SAVE button – RADview saves the service in its database and downloads the configuration to the network. The service is now ready and from this point on, the system monitors the service and collects statistics info, which is then presented in periodic SLA reports.
In the testing portal, you can quickly launch service ethernet activation test per Y.1564 using predefined templates, before handing the service off to your customer. You can also generate test reports and service birth certificates, and export to a PDF format for easy sharing.
The RADview PM module enables ongoing monitoring of Ethernet and IP service performance by collecting and analyzing data on key performance indicators. It allows for real time or periodic SLA reporting on a monthly, weekly, daily, or hourly basis. It can even present the data in 15-minute cycles.
The RADview PM is easy to navigate and understand. It includes a performance dashboard with an aggregated view showing all monitored services and all KPI graphs. From the dashboard, users can access data per service over time. In addition to the intuitive graphs, service status is displayed in green when it conforms to SLA terms, and red when it does not. Metrics include Y.1731 frame delay, delay variation, packet loss, and availability, as well as TWAMP-based Layer 3 performance monitoring for IP services.
For service providers wishing to offer SLA reporting services to their premium customers, the RADview PM portal enables restricted visibility on relevant metrics to end users.
Let’s take a look now at the Distributed NFV domain Orchestrator for the network edge. It follows the ETSI MANO architecture and uses the OpenStack framework to manage the physical and virtualized resources required to effectively run Distributed NFV. It installs virtual network functions, such as routing, encryption, firewall, and more, on RAD’s vCPE devices. It also manages the repository of VNFs, with data on vendor, usage and system requirements for each. Service providers can download and provision multiple VF services, by simply selecting a vCPE, then dragging and dropping the virtualized function into the service.
Let’s take a look now at the advanced user interface of RADview.
The alarms dashboard provides an intuitive summary of all relevant events and alarms, with an optional drill down view to perform fault management for each event.
The topology map allows you to easily navigate the network, perform quick actions, search for devices and tunnels, and more.
The inventory section allows you to see all devices, down to the port and card-level, as well as virtual machines and VNFs.
When provisioning services and applications with the Service Manager module, you get a visual representation of the entire path. The split screen view provides easy access to OAM settings, service activation tests, and all other service details.
And in the testing portal, you can quickly launch service activation test per Y.1564 using predefined templates, as well as generate test reports and service birth certificates, and export to a PDF format for easy sharing.
RAD’s RADview allows operators to manage current and future networks and provides a smooth migration path to programmable networks. Sophisticated yet extremely simple to operate, it uses state of the art tools to deliver the most advanced user experience. As a modular and open system, it includes all functionality required to make daily NOC operations easier and more efficient, to test and roll out new services quickly, and to ensure complete performance visibility.





